Balanced search tree (AVL Tree)
Binary search tree
- find(), insert() and delete() all walk down a single path
- Worst-case: height of the tree An unbalanced tree with n nodes may have height
AVL Tree
- Balanced trees have height
- Using rotations, we can maintain height balance
- Height balanced trees have height
- find(), insert() and delete() all walk down a single path, take time
- Minimum number of node
- Maximum number of nodes
Example for creation of AVL Tree
Implementation
class AVLTree:
# Constructor:
def __init__(self,initval=None):
self.value = initval
if self.value:
self.left = AVLTree()
self.right = AVLTree()
self.height = 1
else:
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.height = 0
return
def isempty(self):
return (self.value == None)
def isleaf(self):
return (self.value != None and self.left.isempty() and self.right.isempty())
def leftrotate(self):
v = self.value
vr = self.right.value
tl = self.left
trl = self.right.left
trr = self.right.right
newleft = AVLTree(v)
newleft.left = tl
newleft.right = trl
self.value = vr
self.right = trr
self.left = newleft
return
def rightrotate(self):
v = self.value
vl = self.left.value
tll = self.left.left
tlr = self.left.right
tr = self.right
newright = AVLTree(v)
newright.left = tlr
newright.right = tr
self.right = newright
self.value = vl
self.left = tll
return
def insert(self,v):
if self.isempty():
self.value = v
self.left = AVLTree()
self.right = AVLTree()
self.height = 1
return
if self.value == v:
return
if v < self.value:
self.left.insert(v)
self.rebalance()
self.height = 1 + max(self.left.height, self.right.height)
if v > self.value:
self.right.insert(v)
self.rebalance()
self.height = 1 + max(self.left.height, self.right.height)
def rebalance(self):
if self.left == None:
hl = 0
else:
hl = self.left.height
if self.right == None:
hr = 0
else:
hr = self.right.height
if hl - hr > 1:
if self.left.left.height > self.left.right.height:
self.rightrotate()
if self.left.left.height < self.left.right.height:
self.left.leftrotate()
self.rightrotate()
self.updateheight()
if hl - hr < -1:
if self.right.left.height < self.right.right.height:
self.leftrotate()
if self.right.left.height > self.right.right.height:
self.right.rightrotate()
self.leftrotate()
self.updateheight()
def updateheight(self):
if self.isempty():
return
else:
self.left.updateheight()
self.right.updateheight()
self.height = 1 + max(self.left.height, self.right.height)
def inorder(self):
if self.isempty():
return([])
else:
return(self.left.inorder()+ [self.value]+ self.right.inorder())
def preorder(self):
if self.isempty():
return([])
else:
return([self.value] + self.left.preorder()+ self.right.preorder())
def postorder(self):
if self.isempty():
return([])
else:
return(self.left.postorder()+ self.right.postorder() + [self.value])
A = AVLTree()
nodes = eval(input())
for i in nodes:
A.insert(i)
print(A.inorder())
print(A.preorder())
print(A.postorder())
Sample Input
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7] #order of insertion
Output
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] #inorder traversal
[4, 2, 1, 3, 6, 5, 7] #preorder traversal
[1, 3, 2, 5, 7, 6, 4] #postorder traveral
Greedy Algorithm
Need to make a sequence of choices to achieve a global optimum
At each stage, make the next choice based on some local criterion
Never go back and revise an earlier decision
Drastically reduces space to search for solutions
Greedy strategy needs a proof of optimality
Example :
- Dijkstra's
- Prim's
- Kruskal's
- Interval scheduling
- Minimize lateness
- Huffman coding
Interval scheduling
Scenario example
▪ IIT Madras has a special video classroom for delivering online lectures
▪ Different teachers want to book the classroom
▪ Slots may overlap, so not all bookings can be honored
▪ Choose a subset of bookings to maximize the number of teachers who get to use the room
Algorithm
- Sort all jobs which based on end time in increasing order.
- Take the interval which has earliest finish time.
- Repeat next two steps till you process all jobs.
- Eliminate all intervals which have start time less than selected interval’s end time.
- If interval has start time greater than current interval’s end time, at it to set. Set current interval to new interval.
Implementation
def tuplesort(L, index):
L_ = []
for t in L:
L_.append(t[index:index+1] + t[:index] + t[index+1:])
L_.sort()
L__ = []
for t in L_:
L__.append(t[1:index+1] + t[0:1] + t[index+1:])
return L__
def intervalschedule(L):
sortedL = tuplesort(L, 2)
accepted = [sortedL[0][0]]
for i, s, f in sortedL[1:]:
if s > L[accepted[-1]][2]:
accepted.append(i)
return accepted
#(job id,start time, finish time) in each tuple of list L
L = [(0, 1, 2),(1, 1, 3),(2, 1, 5),(3, 3, 4),(4, 4, 5),(5, 5, 8),(6, 7, 9),(7, 10, 13),(8, 11, 12)]
print(len(intervalschedule(L)))
Output
4
Analysis
- Initially, sort n bookings by finish time —
- Single scan,
- overall
Example
In the table below, we have 8 activities with the corresponding start and finish times, It might not be possible to complete all the activities since their time frame can conflict. For example, if any activity starts at time 0 and finishes at time 4, then other activities can not start before 4. It can be started at 4 or afterwards.
What is the maximum number of activities which can be performed without conflict?
| Activity | Start time | Finish time |
|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 2 |
| B | 3 | 4 |
| C | 0 | 6 |
| D | 1 | 4 |
| E | 4 | 5 |
| F | 5 | 9 |
| G | 9 | 11 |
| H | 8 | 10 |
Answer
5
Minimize lateness
Scenario example
▪ IIT Madras has a single 3D printer
▪ A number of users need to use this printer
▪ Each user will get access to the printer, but may not finish before deadline
▪ Goal is to minimize the lateness
Algorithm
Sort all job in ascending order of deadlines
Start with time t = 0
For each job in the list
- Schedule the job at time t
- Finish time = t + processing time of job
- t = finish time
Return (start time, finish time) for each job
Implementation
from operator import itemgetter
def minimize_lateness(jobs):
schedule =[]
max_lateness = 0
t = 0
sorted_jobs = sorted(jobs,key=itemgetter(2))
for job in sorted_jobs:
job_start_time = t
job_finish_time = t + job[1]
t = job_finish_time
if(job_finish_time > job[2]):
max_lateness = max (max_lateness, (job_finish_time - job[2]))
schedule.append((job[0],job_start_time, job_finish_time))
return max_lateness, schedule
jobs = [(1, 3, 6), (2, 2, 9), (3, 1, 8), (4, 4, 9), (5, 3, 14), (6, 2, 15)]
max_lateness, sc = minimize_lateness(jobs)
print ("Maximum lateness is :" + str(max_lateness))
for t in sc:
print ('JobId= {0}, start time= {1}, finish time= {2}'.format(t[0],t[1],t[2]))
Output
Maximum lateness is :1
JobId= 1, start time= 0, finish time= 3
JobId= 3, start time= 3, finish time= 4
JobId= 2, start time= 4, finish time= 6
JobId= 4, start time= 6, finish time= 10
JobId= 5, start time= 10, finish time= 13
JobId= 6, start time= 13, finish time= 15
Analysis
- Sort the requests by D(i) —
- Read all schedule in sorted order —
- overall
Huffman Algorithm
Algorithm
- Calculate the frequency of each character in the string.
- Sort the characters in increasing order of the frequency.
- Make each unique character as a leaf node.
- Create an empty node z. Assign the minimum frequency to the left child of z and assign the second minimum frequency to the right child of z. Set the value of the z as the sum of the above two minimum frequencies.
- Remove these two minimum frequencies from Q and add the sum into the list of frequencies.
- Insert node z into the tree.
- Repeat steps 3 to 5 for all the characters.
- For each non-leaf node, assign 0 to the left edge and 1 to the right edge.
Example
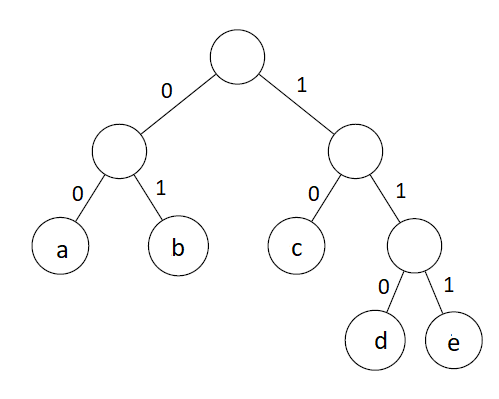
Implementation
class Node:
def __init__(self,frequency,symbol = None,left = None,right = None):
self.frequency = frequency
self.symbol = symbol
self.left = left
self.right = right
# Solution
def Huffman(s):
huffcode = {}
char = list(s)
freqlist = []
unique_char = set(char)
for c in unique_char:
freqlist.append((char.count(c),c))
nodes = []
for nd in sorted(freqlist):
nodes.append((nd,Node(nd[0],nd[1])))
while len(nodes) > 1:
nodes.sort()
L = nodes[0][1]
R = nodes[1][1]
newnode = Node(L.frequency + R.frequency, L.symbol + R.symbol,L,R)
nodes.pop(0)
nodes.pop(0)
nodes.append(((L.frequency + R.frequency, L.symbol + R.symbol),newnode))
for ch in unique_char:
temp = newnode
code = ''
while ch != temp.symbol:
if ch in temp.left.symbol:
code += '0'
temp = temp.left
else:
code += '1'
temp = temp.right
huffcode[ch] = code
return huffcode
s = 'abbcaaaabbcdddeee'
res = Huffman(s)
for char in sorted(res):
print(char,res[char])
Output
a 10
b 01
c 110
d 111
e 00
Huffman Implementation using Min Heap
Contribute by:- Jivitesh Sabharwal
class min_heap:
def __init__(self,nodes):
self.nodes = nodes
self.size =len(nodes)
self.create_min_heap()
def isempty(self):
return len(self.nodes) == 0
def min_heapify(self,s):
l = 2*s + 1
r = 2*s + 2
small = s
if l<self.size and self.nodes[l][0][0] < self.nodes[small][0][0]:
small = l
if r<self.size and self.nodes[r][0][0] < self.nodes[small][0][0]:
small = r
if small != s:
self.nodes[small],self.nodes[s] = self.nodes[s],self.nodes[small]
self.min_heapify(small)
def create_min_heap(self):
for i in range((self.size//2)-1,-1,-1):
self.min_heapify(i)
def insert_min(self,v):
self.nodes.append(v)
self.size += 1
index = self.size -1
while(index > 0):
parent = (index-1)//2
if self.nodes[parent][0][0] > self.nodes[index][0][0]:
self.nodes[parent],self.nodes[index] = self.nodes[index],self.nodes[parent]
index = parent
else:
break
pass
def del_minheap(self):
item = None
if self.isempty():
return item
self.nodes[0],self.nodes[-1] = self.nodes[-1],self.nodes[0]
item = self.nodes.pop()
self.size -= 1
self.min_heapify(0)
return item
class Node:
def __init__(self,frequency,symbol = None,left = None,right=None):
self.frequency = frequency
self.symbol = symbol
self.left = left
self.right = right
def Huffman(s):
freqlist = []
huffcode = {}
char = list(s)
unique_char = set(char)
for c in unique_char:
freqlist.append((char.count(c),c))
nodes = []
for nd in sorted(freqlist):
nodes.append((nd,(Node(nd[0],nd[1]))))
minheap_nodes = min_heap(nodes)
while(minheap_nodes.size > 1):
L = minheap_nodes.del_minheap()[1]
R = minheap_nodes.del_minheap()[1]
newnode = Node(L.frequency+R.frequency,L.symbol+R.symbol,L,R)
internal_node = tuple(((L.frequency+R.frequency,L.symbol+R.symbol),newnode))
minheap_nodes.insert_min(internal_node)
for ch in unique_char:
temp = newnode
code = ''
while ch!=temp.symbol:
if ch in temp.left.symbol:
code += '0'
temp = temp.left
else:
code+= '1'
temp = temp.right
huffcode[ch] = code
return huffcode
s = 'abbcaaaabbcdddeee'
res = Huffman(s)
for char in sorted(res):
print(char,res[char])
Output
a 10
b 01
c 110
d 111
e 00
Analysis
- At each recursive step, extract letters with minimum frequency and replace by composite letter with combined frequency
- Store frequencies in an array
- Linear scan to find minimum values
, number of recursive calls is - Complexity is
- Instead, maintain frequencies in an heap
- Extracting two minimum frequency letters and adding back compound letter are both
- Complexity drops to