Home Week-7 Week-9
PDSA - Week 8
PDSA - Week 8Divide and conquer Divide and conquer exampleCounting inversionsClosest pair of pointsInteger multiplicationQuick select and Fast selectMedian of Medians(MoM)Fast select using MOMRecursion trees
Divide and conquer
Break up a problem into disjoint subproblems
Combine these subproblem solutions efficiently
Examples
Merge sort
- Split into left and right half and sort each half separately
- Merge the sorted halves
Quicksort
- Rearrange into lower and upper partitions, sort each partition separately
- Place pivot between sorted lower and upper partitions
Divide and conquer example
Counting inversions
Compare your profile with other customers
Identify people who share your likes and dislikes
No inversions – rankings identical
Every pair inverted – maximally dissimilar
Number of inversions ranges from 0 to n(n – 1) / 2
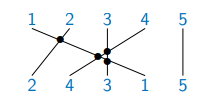
An inversion is a pair (i, j), i < j, where j appears before i
Recurrence:
Implementation
x1def mergeAndCount(A,B):2 (m,n) = (len(A),len(B))3 (C,i,j,k,count) = ([],0,0,0,0)4 while k < m+n:5 if i == m:6 C.append(B[j])7 j += 18 k += 19 elif j == n:10 C.append(A[i])11 i += 112 k += 113 elif A[i] < B[j]:14 C.append(A[i])15 i += 116 k += 117 else:18 C.append(B[j])19 j += 120 k += 121 count += m-i 22 return(C,count)23
24def inversionCount(A):25 n = len(A)26 if n <= 1:27 return(A,0)28 (L,countL) = inversionCount(A[:n//2])29 (R,countR) = inversionCount(A[n//2:])30 (B,countB) = mergeAndCount(L,R)31 return(B,countL + countR + countB)32L = [2,4,3,1,5]33print(inversionCount(L)[1])Output
xxxxxxxxxx114 # 4 is the number of inversions
Closest pair of points
Several objects on screen
Basic step: find closest pair of objects
- For each pair of objects, compute their distance
- Report minimum distance across all pairs
There is a clever algorithm that takes time
Given n points
- Assume no two points have same
- Split the points into two halves by vertical line
- Recursively compute closest pair in each half
- Compare shortest distance in each half to shortest distance across the dividing line
- Assume no two points have same
Recurrence:
Overall:
Pseudocode
xxxxxxxxxx111def ClosestPair(Px,Py):2 if len(Px) <= 3:3 compute pairwise distances4 return closest pair and distance5 Construct (Qx,Qy), (Rx,Ry)6 (q1,q2,dQ) = ClosestPair(Qx,Qy)7 (r1,r2,dR) = ClosestPair(Rx,Ry)8 Construct Sy from Qy,Ry9 Scan Sy, find (s1,s2,dS)10 return (q1,q2,dQ), (r1,r2,QR), (s1,s2,dS)11 #depending on which of dQ, dR, dS is minimumImplementation
xxxxxxxxxx601import math2
3# Returns eucledian disatnce between points p and q4def distance(p, q):5 return math.sqrt(math.pow(p[0] - q[0],2) + math.pow(p[1] - q[1],2))6
7def minDistanceRec(Px, Py):8 s = len(Px)9 # Given number of points cannot be less than 2.10 # If only 2 or 3 points are left return the minimum distance accordingly.11 if (s == 2):12 return distance(Px[0],Px[1])13 elif (s == 3):14 return min(distance(Px[0],Px[1]), distance(Px[1],Px[2]), distance(Px[2],Px[0]))15
16 # For more than 3 points divide the poitns by point around median of x coordinates17 m = s//218 Qx = Px[:m]19 Rx = Px[m:]20 xR = Rx[0][0] # minimum x value in Rx21 22 # Construct Qy and Ry in O(n) rather from Py23 Qy=[]24 Ry=[]25 for p in Py:26 if(p[0] < xR):27 Qy.append(p)28 else:29 Ry.append(p)30
31 # Extract Sy using delta32 delta = min(minDistanceRec(Qx, Qy), minDistanceRec(Rx, Ry))33 Sy = []34 for p in Py:35 if abs(p[0]-xR) <= delta:36 Sy.append(p)37 38 #print(xR,delta,Sy)39 sizeS = len(Sy)40 if sizeS > 1:41 minS = distance(Sy[0], Sy[1])42 for i in range(1, sizeS-1):43 for j in range(i, min(i+15, sizeS-1)):44 minS = min(minS, distance(Sy[i], Sy[j+1]))45 return min(delta, minS)46 else:47 return delta48
49def minDistance(Points):50 Px = sorted(Points)51 Py = Points52 Py.sort(key=lambda x: x[-1])53 #print(Px,Py)54 return round(minDistanceRec(Px, Py), 2)55
56
57
58pts = [(2, 15), (40, 5), (20, 1), (21, 14), (1,4), (3, 11)]59result = minDistance(pts)60print(result)Output
xxxxxxxxxx114.12
Integer multiplication
- Traditional method:
- Naïve divide and conquer strategy:
- Karatsuba’s algorithm:
Implementation
xxxxxxxxxx171# here 10 represent base of input numbers x and y2def Fast_Multiply(x,y,n):3 if n == 1:4 return x * y5 else:6 m = n/27 xh = x//10**m8 xl = x % (10**m)9 yh = y//10**m10 yl = y % (10**m)11 a = xh + xl12 b = yh + yl13 p = Fast_Multiply(xh, yh, m)14 q = Fast_Multiply(xl, yl, m)15 r = Fast_Multiply(a, b, m)16 return p*(10**n) + (r - q - p) * (10**(n/2)) + q 17print(Fast_Multiply(3456,8902,4))Output
xxxxxxxxxx1130765312.0
Quick select and Fast select
- Find the
- Sort in descending order and look at position
- For any fixed
- Median of medians –
- Selection becomes
- Quicksort becomes
Implementation
xxxxxxxxxx231def quickselect(L,l,r,k): # k-th smallest in L[l:r]2 if (k < 1) or (k > r-l):3 return(None)4
5 (pivot,lower,upper) = (L[l],l+1,l+1)6 for i in range(l+1,r):7 if L[i] > pivot: # Extend upper segment8 upper = upper + 19 else: # Exchange L[i] with start of upper segment10 (L[i], L[lower]) = (L[lower], L[i])11 (lower,upper) = (lower+1,upper+1)12 (L[l],L[lower-1]) = (L[lower-1],L[l]) # Move pivot13 lower = lower - 114
15 # Recursive calls16 lowerlen = lower - l17 if k <= lowerlen:18 return(quickselect(L,l,lower,k))19 elif k == (lowerlen + 1):20 return(L[lower])21 else:22 return(quickselect(L,lower+1,r,k-(lowerlen+1)))23print(quickselect([5,3,7,2,1],0,5,2))Output
xxxxxxxxxx112
Median of Medians(MoM)
Divide L into blocks of 5
Find the median of each block (brute force)
Let M be the list of block medians
Recursively apply the process to M
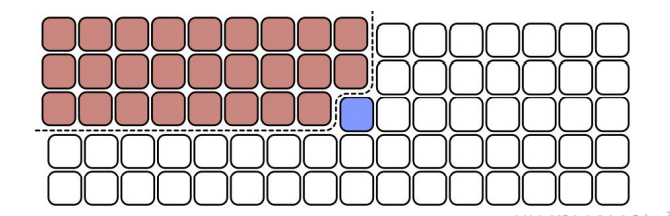
We can visualize the blocks as follows
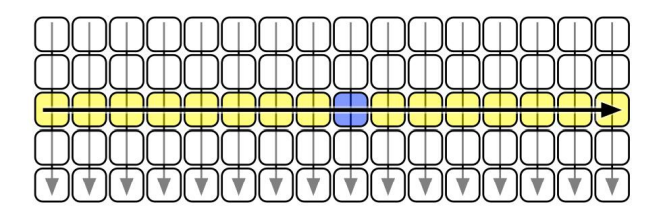
Each block of 5 is arranged in ascending order, top to bottom
Block medians are the middle row
The median of block medians lies between 3len(L)/10 and 7len(L)/10
Implementation
xxxxxxxxxx121def MoM(L): # Median of medians2 if len(L) <= 5:3 L.sort()4 return(L[len(L)//2])5 # Construct list of block medians6 M = []7 for i in range(0,len(L),5):8 X = L[i:i+5]9 X.sort()10 M.append(X[len(X)//2])11 return(MoM(M))12print(MoM([4,3,5,6,2,1,8,9,7,10,13,15,18,17,11]))Output
xxxxxxxxxx118
Fast select using MOM
Implementation
xxxxxxxxxx421def MoM(L): # Median of medians2 if len(L) <= 5:3 L.sort()4 return(L[len(L)//2])5 # Construct list of block medians6 M = []7 for i in range(0,len(L),5):8 X = L[i:i+5]9 X.sort()10 M.append(X[len(X)//2])11 return(MoM(M))12
13
14
15def fastselect(L,l,r,k): # k-th smallest in L[l:r]16 if (k < 1) or (k > r-l):17 return(None)18
19 # Find MoM pivot and move to L[l]20 pivot = MoM(L[l:r])21 pivotpos = min([i for i in range(l,r) if L[i] == pivot])22 (L[l],L[pivotpos]) = (L[pivotpos],L[l])23
24 (pivot,lower,upper) = (L[l],l+1,l+1)25 for i in range(l+1,r):26 if L[i] > pivot: # Extend upper segment27 upper = upper + 128 else: # Exchange L[i] with start of upper segment29 (L[i], L[lower]) = (L[lower], L[i])30 (lower,upper) = (lower+1,upper+1)31 (L[l],L[lower-1]) = (L[lower-1],L[l]) # Move pivot32 lower = lower - 133 34 # Recursive calls35 lowerlen = lower - l36 if k <= lowerlen:37 return(fastselect(L,l,lower,k))38 elif k == (lowerlen + 1):39 return(L[lower])40 else:41 return(fastselect(L,lower+1,r,k-(lowerlen+1)))42print(fastselect([4,3,5,6,2,1,8,9,7,10,13,15,18,17,11],0,15,4))Output
xxxxxxxxxx114
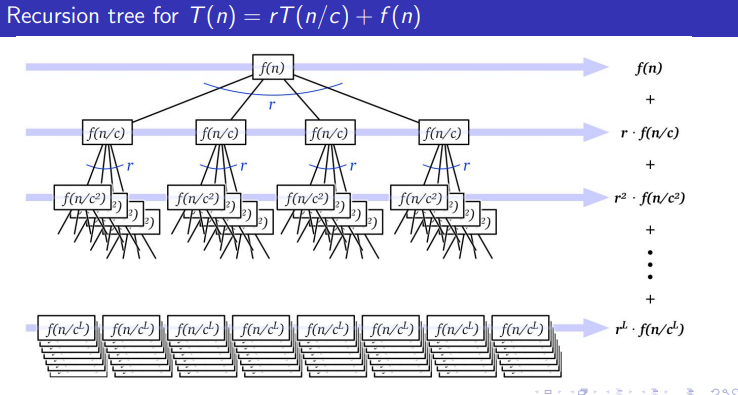
Recursion trees
Recursion tree-Rooted tree with one node for each recursive subproblem
Value of each node is time spent on that subproblem excluding recursive calls
Concretely, on an input of size
- Each recursive call works on a subproblem of size
Resulting recurrence:
Root of recursion tree for
Root has
Each node at level
- Assume, for simplicity, that
- Assume, for simplicity, that